Blogs
Enrich your digital marketing knowledge with our insightful blogs.
Online Live Courses | Offline Courses | Live Webinars | Mentorship

File types indexable by Google
Read more: File types indexable by GoogleGoogle can index the majority of page and file types. You can use the filetype: operator in Google Search to limit results to a specific file type or file extension.

Maintaining your website’s SEO
Read more: Maintaining your website’s SEOEven if your site is already indexed by Google with some knowledge of basics SEO, now you can do even more to boost its visibility. More unusual situations that have an impact on Google Search will be clear as you manage and maintain your website.

Creating helpful, reliable, people first content
Read more: Creating helpful, reliable, people first contentGoogle’s automated ranking systems are built to prioritise delivering relevant, high-quality content that is created with users in mind rather than with an eye toward increasing a site’s PageRank.

Advanced Guide to Search Console
Read more: Advanced Guide to Search ConsoleThe primary focus of your work will determine which report is the most pertinent. On a more general level, it is possible to differentiate between reports that would be most relevant to web developers and those that would be most relevant to SEO specialists, digital marketers, and site administrators.

Get started with Search
Read more: Get started with SearchIt is important to make your content searchable because this is how you will attract more users who are relevant to viewing your content. The process of doing this is known as search engine optimization (SEO), and it can lead to more interested users visiting your website.

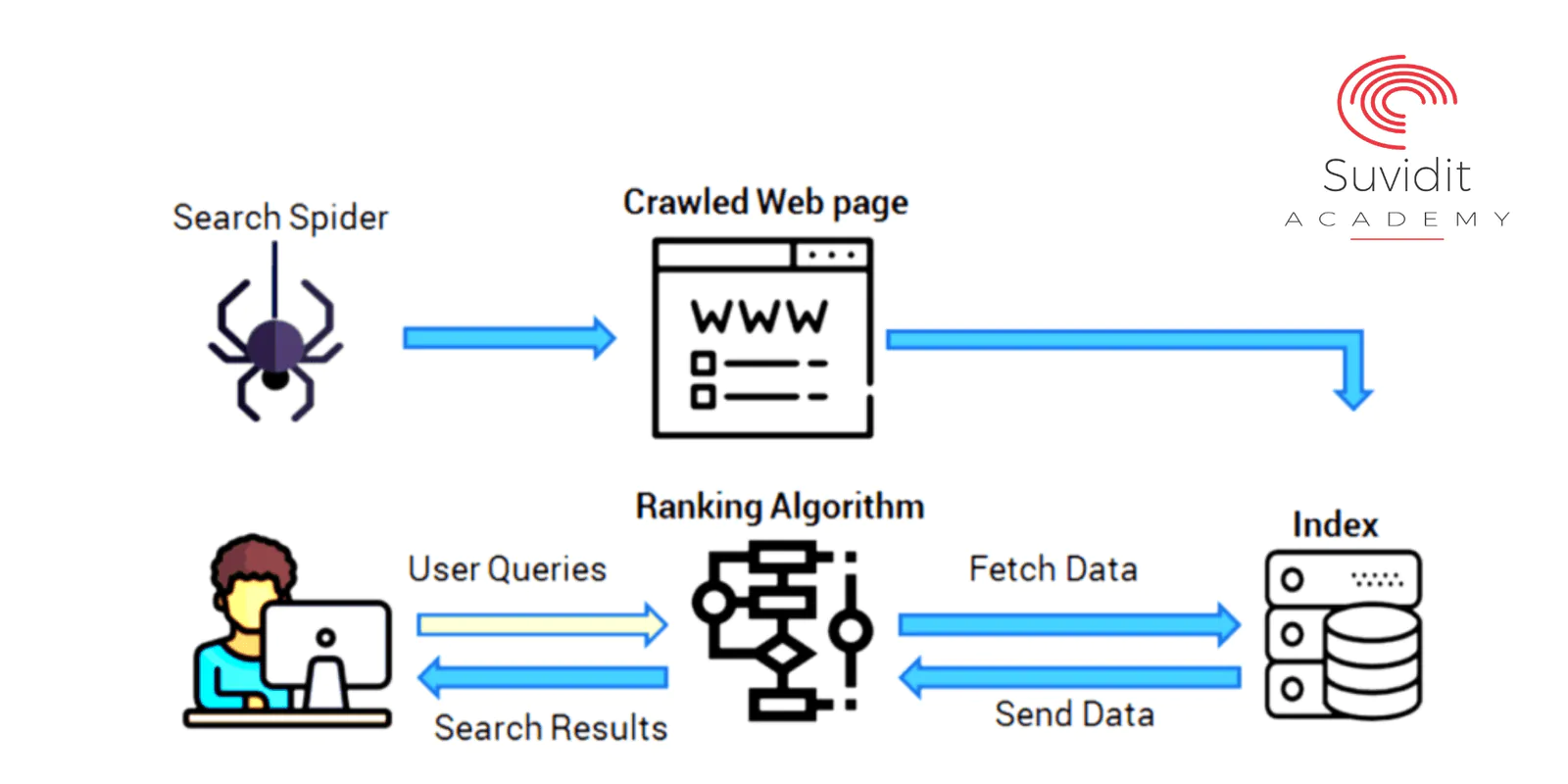
How Search works
Read more: How Search worksWithin the context of your website, the stages of the Search functionality are explained here. If you have this foundational knowledge, you will be better equipped to resolve crawling issues, get your pages indexed, and learn how to optimise the way your site appears in Google Search.

How to Hire SEO Specialist
Read more: How to Hire SEO SpecialistYour website and reputation may be at risk when you hire an SEO, so it’s important to weigh all of your options before making a final decision. Keep in mind that it may take four months to a year after you begin making changes before you begin to see any results.

Marketing Explained at Best
Read more: Marketing Explained at BestDirect Marketing Advertising Public Relation Brand Recognition Customer Feedback Demand & Supply Gap Competition Eating Market Share Restriction for Entering New Market Good Marketing doesn’t feel like a Marketing

How Google Search Works (for beginners)
Read more: How Google Search Works (for beginners)Once Google discovers a page’s URL, it visits the page, or crawls it, to determine what is on it. Google renders the page and analyses its textual and non-textual content, as well as its overall visual layout, in order to determine where it should appear in Search results.